The Lapiplasty procedure is a modern approach designed to correct bunions at their source, restoring natural foot alignment in three dimensions.
Cubital tunnel syndrome (CuTS), also known as ulnar neuropathy, is a condition that affects the ulnar nerve causing pain, numbness, pain, and a variety of other symptoms. The ulnar nerve runs from the neck to the hand and passes through a narrow tunnel of tissue on the inside of the elbow called the cubital tunnel.
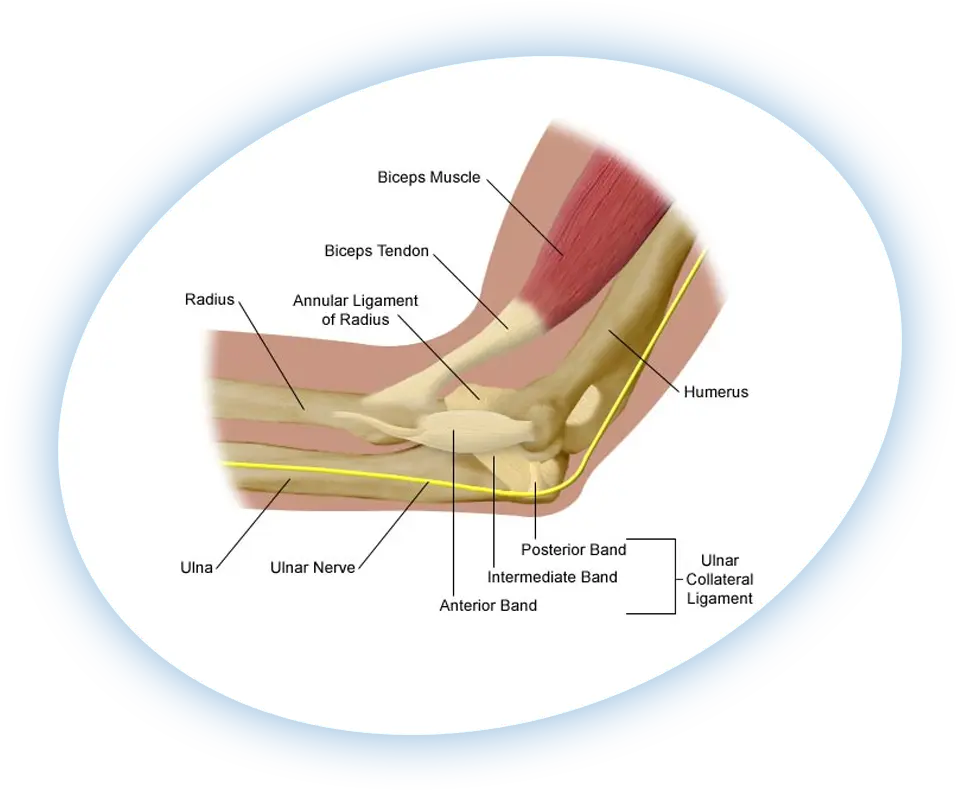




Treatment for cubital tunnel syndrome will depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. In some cases, simply avoiding the activities that cause the symptoms may be enough to alleviate the condition. Other treatments may include:

When diagnosing CuTS, your provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history and perform a physical examination. They may also order diagnostic tests, such as nerve conduction studies or electromyography, to evaluate the function of the ulnar nerve and determine the extent of any nerve damage.



